half life formula for first order reaction
A Product The rate law of zero order kinetics is. Using the concentration-time equation for a second-order reaction we can solve for half-life.

First Order Reaction Definition Examples And Equations
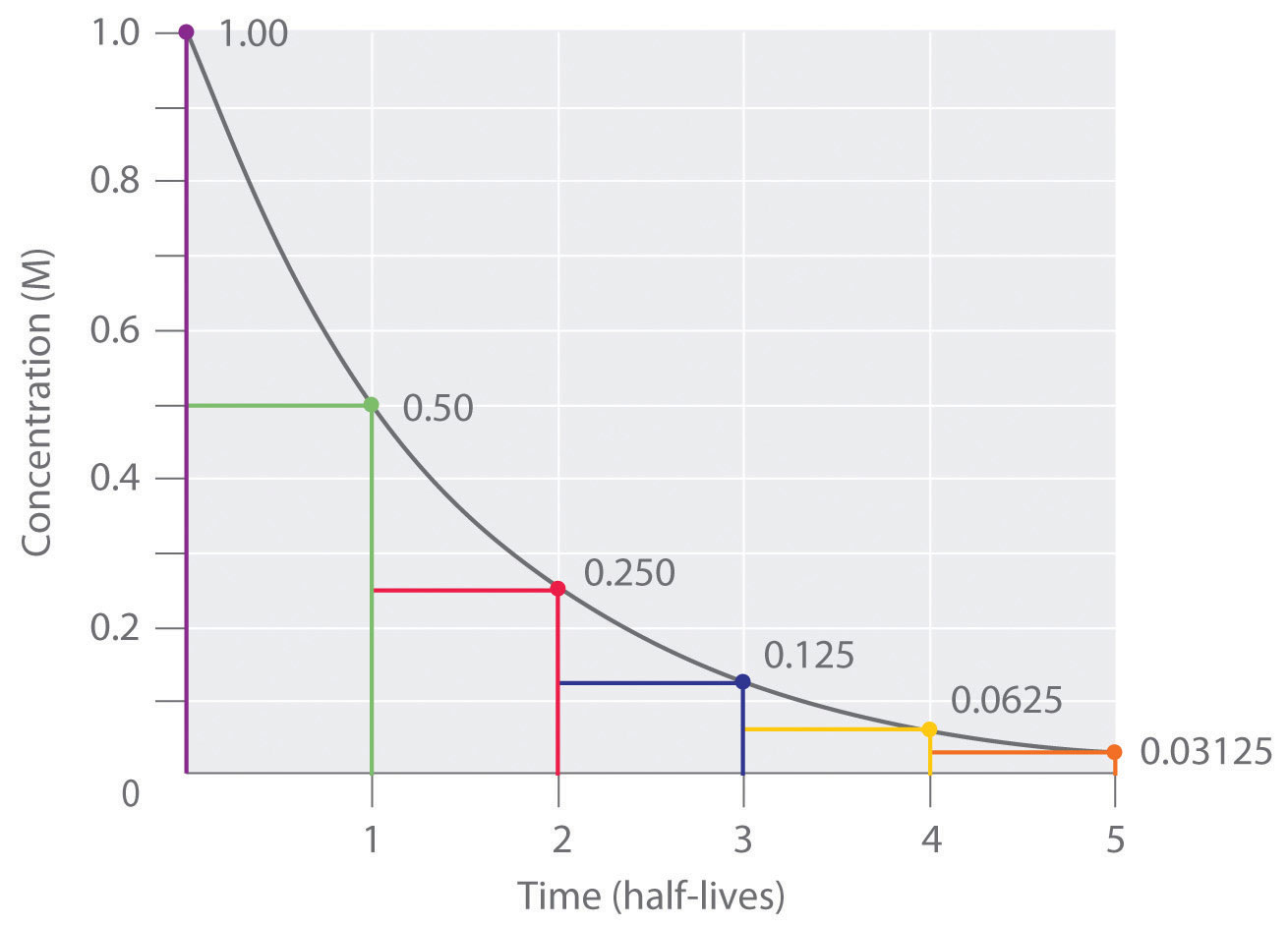
The half life is given the symbol t 12 to denote that it is the time at which the concentration of reactant is one half its initial value.

. Integrating from time 0 to time t the first order integrated rate equation is The half life is the time required for the concentration to drop to one-half its original value. We know that at the half-life time eqt_12 eq the concentration of the reactant will. Substituting these terms into.
The general equation of first-order kinetics. Half-lives for first order reactions Concept Overview. The First Order Half-Life calculator computes the first order half-life based on the temperature dependent rate constant.
The half-life of a reaction is referred to as t 12 unit - seconds The initial reactant concentration is referred to as R 0. The half-life of a second-order reaction is given by the formula 1kR 0. For a first-order reaction the half-life is given by.
In some cases we need to know the initial concentration A o Substitute this information into the equation for the half life of a reaction with this order and solve for t ½. For a first-order reaction the half. For a general reaction.
The formula for a reactions half-life in a second-order reaction is 1k R0. It is essential to note that the half-life formula of a reaction varies with the reactions order. Where A 0 Initial concentration of reactant at timet 0.
This is because radioactive decays always follow first-order kinetics and they can be calculated with an integrated half-life equation. The half-life of a second-order reaction is given by the formula 1kR 0. Where The half-life of a reaction is referred to as t 12 unit - seconds The initial reactant.
What is the expression for Half-Life of a First Order ReactionHere I derive it from the integrated rate lawThe answer is t ln 2 kAsk me questions. For the first order reaction you can plug the definition of the half life into the. The half-life of a first-order reaction is provided by the formula.
Earlier I used to think that it is the time in which concentration of reactant reduces to half of its initial but recently I got a question I dont have that question right now undergoing a first-order reaction with variable volume and then my teacher told that half-life is the time when moles of reactant. The integrated rate law of first-order reaction is given as. How do you derive half-life of a first order reaction.
The order of the reaction or enough information to determine it. We can derive an equation for determining the half-life of a first-order reaction from the alternate form of the integrated rate law as follows. The half-life of a reaction is the time required for a reactant to reach one-half its initial concentration or pressure.
I have a doubt about the meaning of half-life of a first-order reaction. If we set the time t equal to the half-life the corresponding concentration of A at this time is equal to one-half of its initial concentration. Ln A 0 ln A k t.
The half-life of a zero-order reaction the formula is given as t 12 R02k. The half-life formula for various reactions is given below. For a zero-order reaction the mathematical expression that can be employed to determine the half-life is.
Chemical Reaction Half-Life The mathematical formula that can be used to calculate the half-life for a zero-order reaction is t12 R02k. Half life formula for First order reaction. Rearrange the equation so that all concentration dependent terms are collected on one side and all time dependent terms are on the other.
For a second-order reaction the formula for the half-life of the reaction is. Ln N o N t -λt i ii where N t is the concentration of remaining. The mathematical expression that can be employed to determine the half-life for a zero-order reaction is t 12 R 0 2k.
The half-life of a first-order reaction is given as t 12 0693k. A zero order reaction implies that the rate of the reaction does not depend on the concentration of the reactant. The half-life of a first-order reaction is given as t 12 0693k.
Half Life Calculator first order reaction Added Dec 9 2011 by ebola3 in Chemistry This widget calculates the half life of a reactant in a first order reaction. The half life of a reaction is defined as the time it takes for one half of a reactant to disappear. The half-life of a zero-order reaction the formula is given as t 12 R 0 2k.
The rate constant k for the reaction or enough information to determine it. For the first-order reaction the half-life is defined as t 1.

First Order Reactions Study Material For Iit Jee Askiitians

Half Life Of Zero Th 0th Order Reaction Derivation Youtube

Organic Chemistry Half Life And Shelf Life Of Second Order Reaction Chemistry Stack Exchange
Half Life Chemistry Problems Nuclear Radioactive Decay Calculations Practice Examples Youtube

Zero Order Reactions Video Kinetics Khan Academy

First Order Reaction Chemical Kinetics First Order Reaction Youtube

Half Life Of A First Order Reaction Video Khan Academy
Half Life Of A First Order Reaction Video Khan Academy
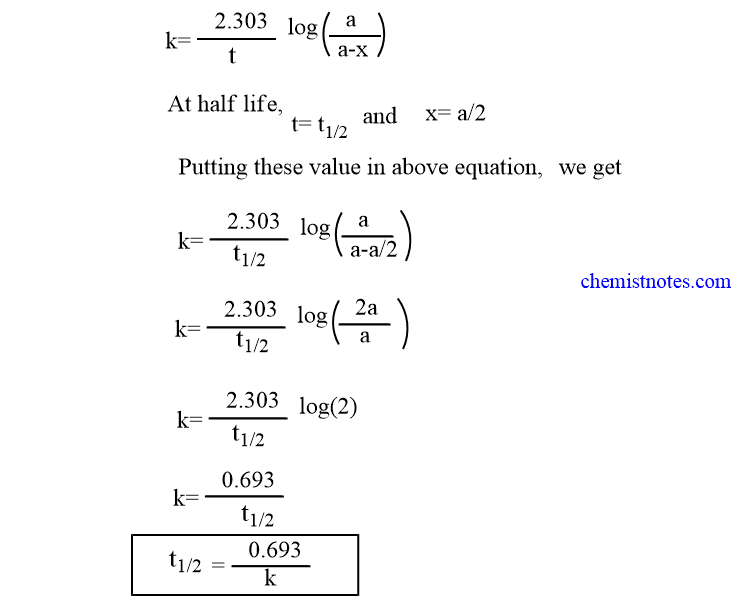
First Order Reaction Definition Example Half Life Period Chemist Notes

Calculate The Half Life Of A First Order Reaction From Their Rate Constants Given Below A 200 S 1 B 2 Min 1 C 4 Year 1
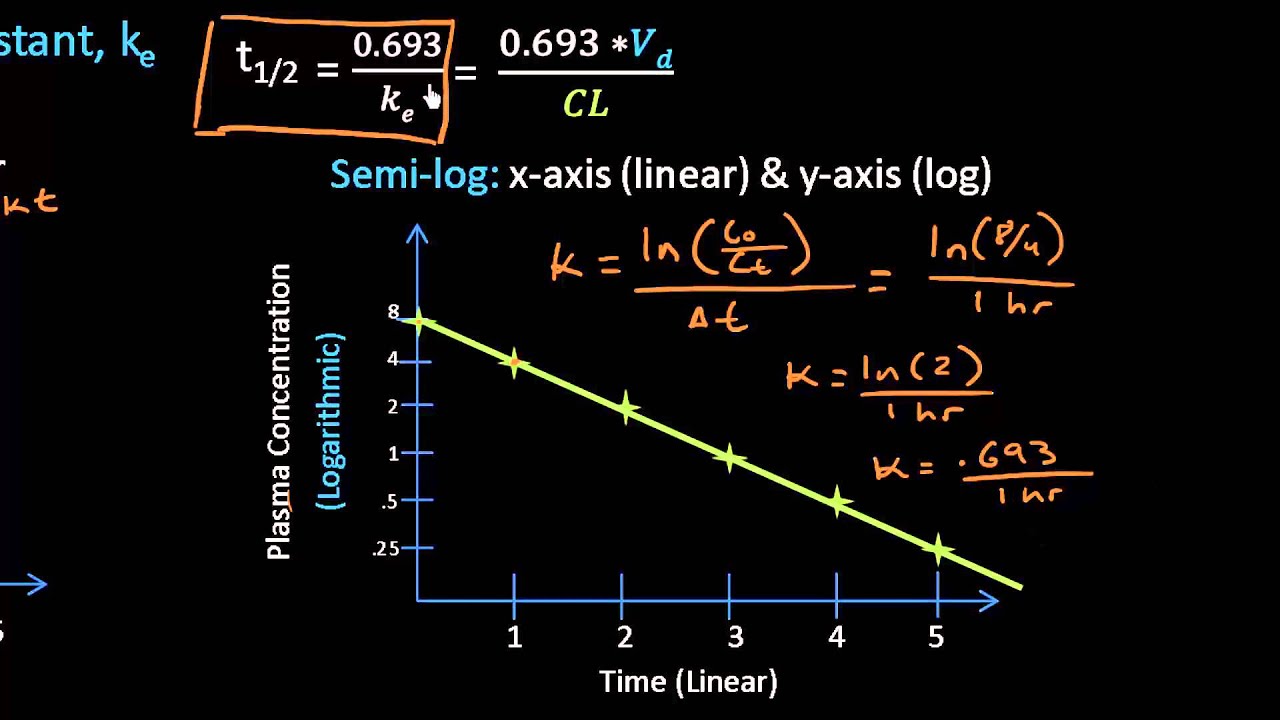
First Order Elimination Rate Constant And Half Life A Closer Look Lect 11 Youtube
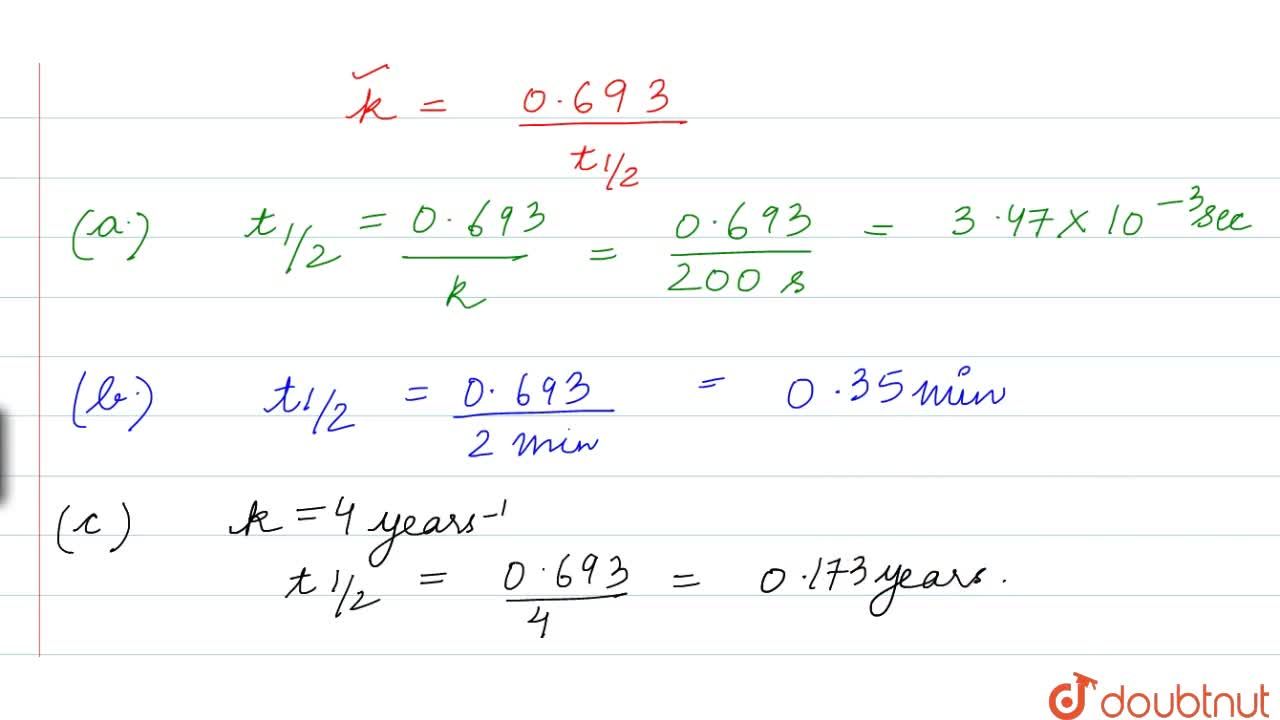
Calculate The Half Life Of A First Order Reaction From Their Rate Constants Given Below A 200s 1 B 2 Mi N 1 C 4years 1

Calculate The Half Life Of A First Order Reaction From Their Rate Constants Given Below A 200 S 1 B 2 Min 1 C 4 Year 1

Integrated Rate Laws Zero First Second Order Reactions Chemical Kinetics Youtube
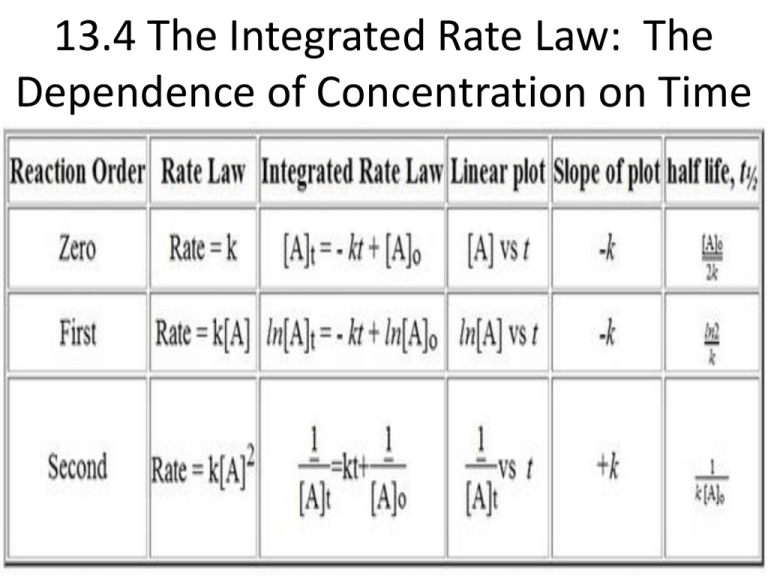
13 4 The Integrated Rate Law The Dependence Of Concentration On